目录
- 目录
- 概念
- 认识 Spring Security OAuth
- 实现与改造 Spring Security OAuth
概念
官方网址
了解Spring Security, OAuth2, Spring Security OAuth
为什么要梳理这三者之间的关系
OAuth协议
注意:以下基于官方文档做出的总结及扩展,如果有不太理解的地方,可以先行在上面官网上了解,欢迎一起讨论
基本思想
这里通常指OAuth2.0(RFC 6749 协议) , OAuth2.0 是OAuth协议的延续版本,OAuth是一个关于授权(authorization)的开放网络标准,但不向后兼容OAuth 1.0即完全废止了OAuth1.0,OAuth 2.0关注客户端开发者的简易性.同时官方对于**2.1, 3.0标准 **也在筹备中, 其中2.1整合和简化 OAuth 2.0 最常用的功能,而3.0 则是一个全新的版本
传统的client-server认证模型中,客户端访问资源服务器受限的资源,资源服务器根据校验客户端的凭证结果,来响应客户端能否访问该资源,如果此时第三方应用也需要对该资源的访问权限,那势必需要将资源的权限与第三方共享
这就带来几个问题和限制
- 第三方应用需要存储资源服务器的凭证信息,以便后续访问该资源,此时密码基本都是明文传输(明不明文其实没关系了,一般情况下就算加密,只要想劫持拿到加密后的串就行),尽管如此,服务器还是得支持密码验证
- 第三方应用程序只要拿到凭证信息,就拥有对资源服务器所有资源访问权限,没有对权限做一个限制或者规定.
- 资源服务器再与第三方终止合作后,不能主动撤销授权,只能通过修改密码的形式去解决
- 凭证信息存在不可信的第三方具有不安全性.
OAuth协议提供授权服务层,将客户端的角色和资源角色分开, 客户端请求访问资源服务器资源,在授权服务层和资源服务器的共同协作管理下,提供属于授权服务层的凭证信息,同时定义该凭证的访问资源服务器的资源,在更高一层解决了前面提出的问题,这个客户端得到的凭证是一个特定属性,特定范围,特定生命周期的字符串,也就是令牌了,这个令牌也代表了资源服务器所允许的访问.资源服务器没有授权的资源,在授权服务层是不会允许访问的,这个也是令牌的一个核心的思想
角色
在OAuth中角色分为四种
- 资源所有者(Resource Owner) 能够授予对受保护资源的访问权限的实体,当资源所有者是个一个人时,也称为最终用户
- 资源服务器(Resource Server) 提供受保护资源的服务器,并托管给授权服务器,能够使用令牌接受和响应访问资源的请求
- 客户端(Clinet) 也就是常说的用户,代表资源所有者定义出来的能够访问受保护资源的一个泛指的概念,如网易云音乐客户端,网页端等等
- 授权服务器(Authorization Server) 授权服务器在成功验证资源所有者并获得授权后向客户端发放令牌,单个授权服务器可以发放多个资源服务器所允许的令牌,且互不影响. 授权服务器必须做到验证请求以确保所有必需的参数都存在且有效。
角色之间的协调关系(A->F):
标准的基本的授权码模式
+--------+ +---------------+
| |--(A)- Authorization Request ->| Resource |
| | | Owner |
| |<-(B)-- Authorization Grant ---| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(C)-- Authorization Grant -->| Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<-(D)----- Access Token -------| |
| | +---------------+
| |
| | +---------------+
| |--(E)----- Access Token ------>| Resource |
| | | Server |
| |<-(F)--- Protected Resource ---| |
+--------+ +---------------+
流程:
A: 客户端向资源所有者发起请求,资源所有者拿到客户端的相关信息,做出授权
B: 资源所有者返回授权凭证给客户端,此凭证中包含所允许的授权范围及类型
C: 客户端与授权服务器进行身份认证,并提供授权凭证许可获取访问令牌
D: 授权服务器对客户端身份验证通过后颁发访问令牌
E: 客户端使用访问令牌请求访问资源服务器受保护的资源,
F: 资源服务器验证令牌,通过后返回所请求的资源
令牌
生成令牌的前提
客户端在得到令牌及使用令牌请求中,需要保证令牌的安全,且仅在授权服务器与客户端之前使用,同时授权服务器需要保证令牌不会因为其他方式修改或者生成后的令牌仍然能继续使用,协议中定义的令牌分为2种
访问令牌(Access Token)
访问令牌是允许对资源服务器访问的凭证
刷新令牌(Refresh Token)
舒心令牌是和访问令牌同步返回的,但也是一个可选项,可与不使用刷新令牌,如果使用刷新令牌去刷新,那么在返回新令牌的同时,之前的所有令牌都将会过期
授权类型
Oauth提供的类型有4种 分别是:
授权码类型(Authorization Code )
适用于三方不互信的场景
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
^
|
(B)
+----|-----+ Client Identifier +---------------+
| -+----(A1)-- & Redirection URI --->| |
| User- | | Authorization |
| Agent -+----(B)-- User authenticates --->| Server |
| | | |
| -+----(C0)-- Authorization Code --<| |
+-|----|---+ +---------------+
| | ^ v
(A0) (C1) | |
| | | |
^ v | |
+---------+ | |
| |>---(D)-- Authorization Code ---------' |
| Client | & Redirection URI |
| | |
| |<---(E)----- Access Token -------------------'
+---------+ (w/ Optional Refresh Token)
Note: The lines illustrating steps (A), (B), and (C) are broken into
two parts as they pass through the user-agent.
流程:
A: 客户端携带clientId, scope, redirectionURI, local state 等通过资源所有者所指定的用户代理定向到授权端点,一旦拒绝就会重定向回redirectionURI
B: 授权服务器验证资源所有者(通过用户代理),并确定资源所有者是允许还是拒绝客户端的请求
C: 授权服务器使用提供的 redirectionURI和客户端提供的信息将用户代理重定向回客户端(基于redirectionURI)并携带授权码在URI片段中
D: 客户端通过授权码及用于获取授权的redirectionURI请求授权服务器并获取令牌
E: 授权服务器对客户端的授权码及redirectionURI 进行匹配身份验证,如果符合之前保存的数据[1],
则返回访问令牌和可选的重定向令牌给客户端,用户通过令牌去访问资源
简化模式/隐式授权(Implicit)
同样适用于三方不互信的场景,但是用于没有服务器端的第三方单页面应用,因为没有服务器端就无法接收授权码
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
^
|
(B)
+----|-----+ Client Identifier +---------------+
| -+----(A)-- & Redirection URI --->| |
| User- | | Authorization |
| Agent -|----(B)-- User authenticates -->| Server |
| | | |
| |<---(C)--- Redirection URI ----<| |
| | with Access Token +---------------+
| | in Fragment
| | +---------------+
| |----(D)--- Redirection URI ---->| Web-Hosted |
| | without Fragment | Client |
| | | Resource |
| (F) |<---(E)------- Script ---------<| |
| | +---------------+
+-|--------+
| |
(A) (G) Access Token
| |
^ v
+---------+
| |
| Client |
| |
+---------+
Note: The lines illustrating steps (A) and (B) are broken into two
parts as they pass through the user-agent.
流程:
和授权模式相比取消了授权过程,直接获取token
A: 客户端携带clientId, scope, redirectionURI, local state 等通过资源所有者所指定的用户代理定向到授权端点,一旦拒绝就会重定向回redirectionURI
B: 授权服务器验证资源所有者(通过用户代理),并确定资源所有者是允许还是拒绝客户端的请求[1:1]
C: 授权服务器使用提供的 redirectionURI和客户端提供的信息将用户代理重定向回客户端(基于redirectionURI)并携带访问令牌在URI片段中
D: 用户代理通过向Web托管的客户端资源发出请求来遵循重定向指令,用户代理保存片段信息
E: Web托管的客户端资源返回能够访问的完整redirectionURI,包括用户代理中保留的片段信息,提取片段中的访问令牌及其他信息
F: 用户代理在本地执行由Web托管的客户端资源提供的脚本,获取访问令牌
G:用户代理将访问令牌返回给客户端
可以看出,简化模式中没有refreshToken相关信息,OAuth也明确了不允许颁发刷新令牌
密码模式(Resource Owner Password Credentials)
适用于资源所有者与客户端具有信任关系的情况,一般是在一个系统中,同时也是一个适用于能够获取资源所有者凭据(用户名和密码,通常使用交互式表单)的客户端或直接身份验证方案(例如 HTTP Basic 或 Digest身份验证)将现有客户端迁移到 OAuth(方法是将存储的凭据转换为访问令牌)的最好方案.
即客户端直接向用户获取账号密码(不安全),之后向授权服务器获取token,第适合自家体系应用开发
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
v
| Resource Owner
(A) Password Credentials
|
v
+---------+ +---------------+
| |>--(B)---- Resource Owner ------->| |
| | Password Credentials | Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<--(C)---- Access Token ---------<| |
| | (w/ Optional Refresh Token) | |
+---------+ +---------------+
流程:
A: 资源所有者向客户端提供其用户名和密码。
B: 客户端通过包含从资源所有者收到的凭据,从授权服务器的令牌端点请求访问令牌。发出请求时,客户端向授权服务器进行身份验证。
C: 授权服务器对客户端进行身份验证并验证资源所有者凭据,如果有效,则颁发访问令牌
客户端模式(Client Credentials)
客户端直接通过客户端认证(比如client_id和client_secret)从认证服务器获取访问令牌,这种模式是最方便但最不安全的模式。因此这就要求我们对client完全的信任,而client本身也是安全的。因此这种模式一般用来提供给我们完全信任的服务器端服务。比如,合作方系统对接,拉取一组用户信息
+---------+ +---------------+
| | | |
| |>--(A)- Client Authentication --->| Authorization |
| Client | | Server |
| |<--(B)---- Access Token ---------<| |
| | | |
+---------+ +---------------+
流程:
A: 客户端向授权服务器进行身份验证,并从令牌端点请求访问令牌。
B: 授权服务器对客户端进行身份验证,如果有效,则颁发
定义
OAuth协议中 定义大概分为三部分
- 请求格式 -> 参数类型,概念及是否为必填项
- 响应格式 -> 响应定义及字段
- 异常响应
其中基本上支持协议的都会取按照定义去实现,但是错误响应一般是不怎么了解的,所以这里对基本异常响应做些释义,除此之外我们也可以自定义异常,这个后面分析
授权服务器以 HTTP 400(异常请求)状态代码(除非另有说明进行响应,并在响应中包含以下参参数
| error | error_description | error_url | 释义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| invalid_request | - | - | 1.请求缺少必需的参数,包括不受支持的参数值(授权类型除外) 2.重复参数 3.包括多个凭据 4.使用一种以上的机制来验证客户端,或者格式错误 |
| invalid_client | - | - | 客户端身份验证失败,clientId不存在 |
| invalid_grant | - | - | 提供的授权授权(例如,授权、代码、资源所有者凭证.刷新令牌) 无效、过期、已撤销、与授权请求中使用的重定向URI不匹配或者已发布给另一个客户端 |
| unauthorized_client | - | - | 客户端没有权限使用所提交的clientId(每个客户端都事先会有定义在数据库中) |
| unsupported_grant_type | - | - | 认证服务器不支持该grant_type ,一般是没有对应的Granter定义去处理 |
| invalid_scope | - | - | 无效的scope参数,考虑排查下是否是当前clientId所支持的scope 如原本存储passenger,driver. 你登录的scope参数是 user |
| unsupported_response_type | - | - | 出现在授权码及隐式授权登录过程中,请检查请参数 |
Spring Security
基本介绍
Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的应用提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。它提供了一组可以在Spring应用上下文中配置的Bean,充分利用了Spring IOC(控制反转Inversion of Control),DI(Dependency Injection 依赖注入)和AOP(面向切面编程)功能,为应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制功能,减少了为企业系统安全控制编写大量重复代码的工作,以Session作为作为交互,控制系统间的认证及授权
在认证框架中 (同名的还有Shiro等) 安全一般分为两步
authentication 和 authorization
authentication 即认证,是为用户建立一个他所声明的用户, 认证这个用户是否能够进行登录
authorization 即授权,指的是一个用户能否在应用中执行某个操作权限,发生在认证通过以后
Spring Security核心就是一组过滤器链,通过各种功能的链路相互配置来保证系统的安全
整体流程
整体流程分为认证流程和授权流程 并且其中最主要的就是认证流程,授权流程因为其特点就暂略可以后续补充
注意点
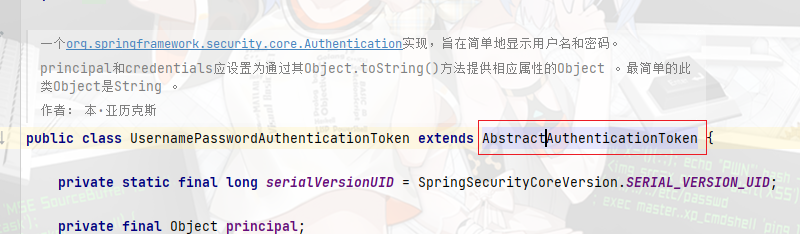
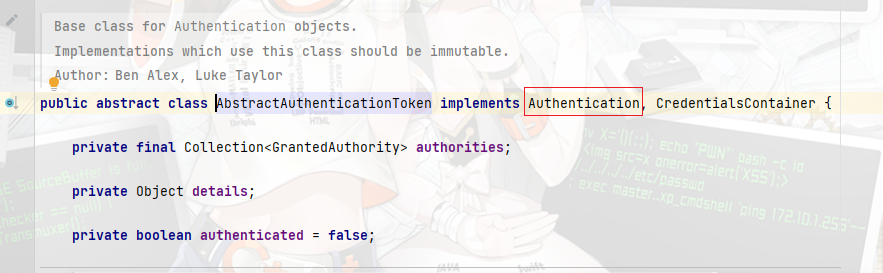
- 首先注意一点,贯穿整体的Token的默认实现是
UserenamePasswordAuthenticationToken类, ,同时从下面截图,这里可以看出其继承了AbstractAuthenticationToken, 而AbstractAuthenticationToken又是Authentication对象的一个实现,这个是后面support方法的依据 - 同时
Authentication对象继承自Principal类代表一个抽象主体身份

- 代码中头部都具体标注了是属于哪个类的方法,但是基本都是实现类的方法,如果对流程不熟悉建议从父类慢慢梳理
认证流程
整体流程
在认证流程大方向上,首先被AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter类拦截并协调行为(经典的模板方法使用)分为 :
(a) 交给UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter等拦截器处理获取Authentication对象
**(b)实现successfulAuthentication()**方法保存Authentication对象到上下文信息中以便后续授权等等使用
//AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter类
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
// 1. 处理并返回Authentication对象
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authenticationResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
// Authentication success
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// 2.将Authentication对象保存起来
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);
}
}
具体分析
(a). 户提交用户名及密码被UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter拦截器处理,并将信息一并封装为UserNamePasswordAuthenticationToken类,提交至认证管理器AuthenticationManager进行认证
//UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类
/**
*登录验证,封装传递的token
*/
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
// postOnly默认为true,此时如果是Post请求就抛出异常
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
//获取用户名
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username : "";
username = username.trim();
//获取密码
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
//将密码和用户名注入Token类中
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
//调用认证方法
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
1. AuthenticationManager 默认实现 ProviderManager整体处理流程
//ProviderManager
/**
* AuthenticationManager默认实现,这里能体现出认证流程的全局思路
*/
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
/*
* 1. 寻找能够support Token的实现 support依据如:
* AnonymousAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication)
*/
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
// 2. 找到能够处理token对象后,委托认证得到完整的Authentication对象
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
// 忽略中间代码 ......
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// 3. 如果认证成功,则发布认证成功事件给Spring ,但是注意这里默认是空实现
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
// 4. 没有认证成功,则抛出异常
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() }, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}
**2.** 由流程可知 ```AuthenticationManager``` 默认实现为```ProviderManager```判断是否有够处理```UserNamePasswordAuthenticationToken```类的**Provider**类,并交付给**Provider**类让其去做认证处理,得到完整的被填充的```Authentication```对象
2.1. AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 类默认使用DaoAuthenticationProvider类处理,但是具体处理流程由AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider统一协调(经典的模板方法使用), 即在获取完用户信息后, 再进行密码的比对,最后返回完整的对象
// DaoAuthenticationProvider
/**
* 获取UserDetails对象
*/
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
/*
* 调用UserDetailService 实现类获取用户信息UserDetails对象,这里的UserDetailService就是我们大展宏图的地方
* 可以从任何渠道(数据库,写死的,缓存的等等)获取这个UserDetails对象,只要你返回的对象符合规则,就没任何问题
*/
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
2.2. 简单的比较密码,依赖于passwordEncoder密码解析器的具体实现
// DaoAuthenticationProvider
/**
* 比较密码
*/
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
//这里比较
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
2.3. 密码比较通过后 填充Authentication对象
// AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider类,实现类会多一步对密码的处理,然后再调用父类
/**
* 填充对象,可以看出返回的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象
*/
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal, Authentication authentication,
UserDetails user) {
// Ensure we return the original credentials the user supplied,
// so subsequent attempts are successful even with encoded passwords.
// Also ensure we return the original getDetails(), so that future
// authentication events after cache expiry contain the details
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal,
authentication.getCredentials(), this.authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
this.logger.debug("Authenticated user");
return result;
}
3. 前面也提到了,事件通知是默认的实现,这个可以方便我们扩展,后面再分析
(b).身份信息认证通过后,生成完整的Authentication对象,并将Authentication对象设置到系统的上下文中,这样在授权阶段就可以获取到 Authentication 认证信息,并利用 Authentication 内的权限信息进行访问控制
//AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter类
/**
* 保存安全上下文信息
*/
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult));
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass()));
}
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
整体认证流程也就结束了.
Spring Security OAuth
实质上为Spring提供对OAuth的支持,根据OAuth协议标准设计的,所以很多概念都可以从OAuth2.0协议中得到, 主要设计目的是为了解决第三方登录之间不可信的问题,用令牌来接替传统的密码模式, 同时提供一个统一认证的入口,将整体系统的结构划分为了 授权服务器, 资源服务器以及第三方,当然授权服务器也可以和资源服务器在一起,整体实现上的结构跟Spring Security实现的思想大同小异
结构
基本概念
在OAuth中大方向上分为两种
一 客户端: 以客户端为一个用户,客户端为最终的操作发起者
二 用户: 用户所属于一个客户端,用户是最终的操作发起者
常用字段说明
scope: 作用域,客户端级别,可以为空也可以为一个集合,代表那些客户端拥有那些权限,但必须配置了才会生效
clientId: 客户端ID,当前客户端的标识
clientSecret: 和客户端对应,代表 客户端的秘钥, 举例 appId 和 appKey的关系
grantType: 授权类型 具体对应某一个类型 一个客户端中可以有多个grantType,代表支持多种授权模式
resourceIds: 资源ID,如果当前资源服务器中设有资源ID, 且客户端配置资源ID集合,则当前客户端无权访问定义外的资源服务器
redirectUri: 在授权码模式下,当前客户端所定义的需要重定向的地址
autoApprove: 在授权码模式下,如果为true 则默认赋予所有scope权限,也可具体赋值scope集合给该属性代表部分权限
OAuth定义的端点
- /oauth/authorize:授权端点
- /oauth/token:令牌端点
- /oauth/confirm_access:用户确认授权提交端点
- /oauth/error:授权服务错误信息端点
- /oauth/check_token:用于资源服务访问的令牌解析端点
- /oauth/token_key:提供公有密匙的端点,如果使用JWT令牌的话
主要来了解令牌端点来梳理认证流程
令牌端点 TokenEndpoint
1.认证端点负责定义整体流程走向,最后调用TokenGranter获得OAuth2AccessToken
其中getAccessToken()方法作用是代理GET请求,但是默认实现的allowedRequestMethods 里是不支持GET请求的,所以实质上只支持POST请求即**postAccessToken()**方法
- 首先从请求参数中拿到clientId
- 再从数据源中查询获取当前请求的clientId所定义的
ClientDetails对象 - 再构造
TokenRequest对象 - 如果当前clientId不为空且不与数据库中定义的不同抛出
InvalidClientException无效的客户端异常 - 如果
clientDetails对象不为空,校验当前clientId 对应scope集合是否全部有效,如果有一个为空或者跟数据库中定义的scope不匹配,则抛出异常(注意此条件之前没有走清洗scope的哪一步,就算走了也有可能为空) - 如果构造的
tokenRequest即请求参数中不存在grantType那么抛出InvalidRequestExceptiongrant type 不存在 - 如果是隐式授权模式,那么也不支持访问该端点,因为implicit被设计成是没有授权这一步的, response_type=token
- 如果是授权码模式,就需要确认当前定义的scope集合为空,不能让注入scope集合,同时从**IsAuthCodeRequest()**方法可以看出,到达端点之前,前提是存在code 即授权码
- 如果是刷新token请求,注入刷新token请求所定义的默认scope集合
// TokenEndpoint类 这个是没有@Controller注解的,但是有@FrameworkEndpoint注解(但仅用于框架提供的端点)
/**
* 1.访问端点GET
* 作用 GET 请求转POST 请求,当然默认实现的allowedRequestMethods 里是不支持GET请求的
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessToken> getAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map<String, String> parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
// allowedRequestMethods 一个HttpMethod 的 SET集合,默认实现中只有POST请求
if (!allowedRequestMethods.contains(HttpMethod.GET)) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("GET");
}
// 调用post方法
return postAccessToken(principal, parameters);
}
/**
* 2.访问端点POST
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessToken> postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map<String, String> parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
// 客户端访问资源服务器时,会在请求中带上访问令牌。user-agent
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
//拿到clientId
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
// 查询数据库中的ClientDetails对象
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
//创建OAuthTokenRequest对象
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
//如果clientId不为空
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
//如果当前clientId不为空且不与数据库中定义的不同抛出`InvalidClientException`无效的客户端异常
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
//如果有一个为空或者跟数据库中定义的scope不匹配,则抛出异常(注意此条件之前没有走清洗scope的哪一步,就算走了也有可能为空)
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
//如果构造的tokenRequest即请求参数中不存在grantType那么抛出`InvalidRequestException` granttype丢失
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
//如果是隐式授权模式,那么也不支持访问该断点,因为implicit被设计成是没有授权这一步的
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
// 如果是授权码模式,就需要确认当前定义的scope为空,不能让注入scope,同时从IsAuthCodeRequest方法可以看出,到达端点之前前提是存在code 授权码
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections.<String> emptySet());
}
}
// 如果是刷新token请求,注入默认的scope
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) { tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
}
创建TokenRequest,总体思路为
- 如果请求参数里没有clientId,则拿到数据库中的clientId.如果存在clientId但是与数据库中的不符合则抛出异常,
InvalidClientException(无效的ClientId) - 接着从请求参数中拿到grantType授权类型
- 再从请求参数中拿到Scope作用域,因为scope作用域可以有多个,所以定义为Set类型,如果请求参数中不存在则将数据库中scope集合赋值给该对象
- 如果配置的checkUserScopes为true, 默认校验为false, 则将请求的scope集合与当前clientId所赋予的scope集合做对比,达到清洗的目的,只返回当前clientId所定义的scope
// DefaultOAuth2RequestFactory类 OAuth2RequestFactory默认实现.
/**
* 创建TOkenRequest..
*/
public TokenRequest createTokenRequest(Map<String, String> requestParameters, ClientDetails authenticatedClient) {
String clientId = requestParameters.get(OAuth2Utils.CLIENT_ID);
if (clientId == null) {
clientId = authenticatedClient.getClientId();
}
else {
if (!clientId.equals(authenticatedClient.getClientId())) {
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
String grantType = requestParameters.get(OAuth2Utils.GRANT_TYPE);
Set<String> scopes = extractScopes(requestParameters, clientId);
TokenRequest tokenRequest = new TokenRequest(requestParameters, clientId, scopes, grantType);
return tokenRequest;
}
/*
* 获取scopeSet集合对象.
*/
private Set<String> extractScopes(Map<String, String> requestParameters, String clientId) {
Set<String> scopes = OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(requestParameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE));
ClientDetails clientDetails = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
if ((scopes == null || scopes.isEmpty())) {
scopes = clientDetails.getScope();
}
//如果配置的checkUserScopes为true ,则将请求的scope与当前clientId所赋予的scope做对比,判断是否存在..
if (checkUserScopes) {
scopes = checkUserScopes(scopes, clientDetails);
}
return scopes;
}
/**
* 默认是进不来的,因为checkUserScopes为false,可以算是清洗scope..
*/
private Set<String> checkUserScopes(Set<String> scopes, ClientDetails clientDetails) {
if (!securityContextAccessor.isUser()) {
return scopes;
}
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
Set<String> authorities = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(securityContextAccessor.getAuthorities());
for (String scope : scopes) {
if (authorities.contains(scope) || authorities.contains(scope.toUpperCase())
|| authorities.contains("ROLE_" + scope.toUpperCase())) {
result.add(scope);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 校验当前scope是否有效,为空或者有一个跟数据库中定义的scope不匹配,则抛出异常(注意此条件之前没有走清洗scope的哪一步,就算走了也有可能为空)
*/
private void validateScope(Set<String> requestScopes, Set<String> clientScopes) {
if (clientScopes != null && !clientScopes.isEmpty()) {
for (String scope : requestScopes) {
if (!clientScopes.contains(scope)) {
throw new InvalidScopeException("Invalid scope: " + scope, clientScopes);
}
}
}
if (requestScopes.isEmpty()) {
throw new InvalidScopeException("Empty scope (either the client or the user is not allowed the requested scopes)");
}
}
2.走到TokenGranter这步,循环判断具体怎么选择那个子类去处理当前传递的grantType取决于CompositerTokenGranter类
public class CompositeTokenGranter implements TokenGranter {
private final List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters;
public CompositeTokenGranter(List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters) {
this.tokenGranters = new ArrayList<TokenGranter>(tokenGranters);
}
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
for (TokenGranter granter : tokenGranters) {
OAuth2AccessToken grant = granter.grant(grantType, tokenRequest);
if (grant!=null) {
return grant;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addTokenGranter(TokenGranter tokenGranter) {
if (tokenGranter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Token granter is null");
}
tokenGranters.add(tokenGranter);
}
}
TokenGranter 令牌授予者,系统中默认定义的为以下几个实现类
AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter 授权码模式
ClientCredentialsTokenGranter 客户端模式
ImplicitTokenGranter 隐式授权模式
RefreshTokenGranter 刷新 token 模式
ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter密码模式
AbstractTokenGranter实现了TokenGranter接口的**grant()**方法,对一些基本的逻辑实现处理主要如下
- 如果当前传递的grantType与
AbstractTokenGranter初始化时grantType 不一致,则返回空 - 从构造的
tokenRequest中获取clientId - 验证当前grantType是否是当前clientId对应
ClientDetails信息所绑定的 - 调用**getAccessToken()**方法,传递
OAuth2Authentication对象通过TokenServices类创建OAuth2AccessToken对象并返回
//AbstractTokenGranter类
/**
*****************注意getAccessToken方法,会调用getOAuth2Authentication方法*****************
* 选择处理的Granter
*/
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
//如果当前传递的grantType与AbstractTokenGranter初始化时grantType 不一致,则返回空
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
// 从构造的tokenRequest中获取clientId
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
// 获取当前clientId 绑定的ClientDetails信息
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
//验证grantType是否是当前clientId对应ClientDetails信息所绑定的
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
/**
* 验证grantType是否是当前clientId对应ClientDetails信息所绑定的
*/
protected void validateGrantType(String grantType, ClientDetails clientDetails) {
Collection<String> authorizedGrantTypes = clientDetails.getAuthorizedGrantTypes();
if (authorizedGrantTypes != null && !authorizedGrantTypes.isEmpty()
&& !authorizedGrantTypes.contains(grantType)) {
throw new InvalidClientException("Unauthorized grant type: " + grantType);
}
}
/**
* *****************注意getAccessToken方法,会调用getOAuth2Authentication方法*****************
* 调用getOAuth2Authentication()对象获取OAuth2Authentication对象
* 获取OAuth2AccessToken对象
*/
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest));
}
/**
* 获取OAuth2Authentication对象
*/
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = requestFactory.createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, null);
}
而上面提到的几个实现类则主要是继承并实现了AbstractTokenGranter类 的**getOAuth2Authentication()**方法,以返回OAuth2Authentication对象.
以ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter类为例子
// ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
Map<String, String> parameters = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(tokenRequest.getRequestParameters());
String username = parameters.get("username");
String password = parameters.get("password");
// Protect from downstream leaks of password
parameters.remove("password");
//构造对应用户token
Authentication userAuth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
((AbstractAuthenticationToken) userAuth).setDetails(parameters);
try {
// 这里就去使用AuthenticationManager 去寻找 支持当前grantType 支持 的Provider
userAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(userAuth);
}
catch (AccountStatusException ase) {
throw new InvalidGrantException(ase.getMessage());
}
catch (BadCredentialsException e) {
throw new InvalidGrantException(e.getMessage());
}
//如果还为空,抛出认证异常.
if (userAuth == null || !userAuth.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Could not authenticate user: " + username);
}
// 返回OAuth使用的OAuth2Authentication
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getRequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, userAuth);
}
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider默认实现类DaoAuthenticationProvider去处理获取用户信息,验证用户密码是否匹配,创建Authentication对象,是不是感觉这一步很熟悉,没错,这一步就实际的回到了Spring Security的处理逻辑,AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider协调如何实现上述流程
即 处理用户信息使用UserDetailService 获取,实现类可以是这几种 缓存/定义的clientDetails类中,内存中/数据库中
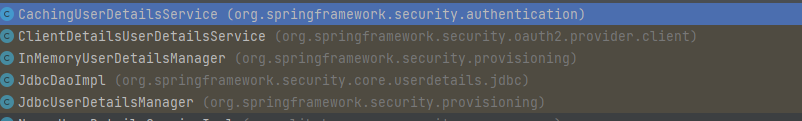
获取用户信息后校验密码是否匹配,校验方式取决去对PasswordEncoder类的实现
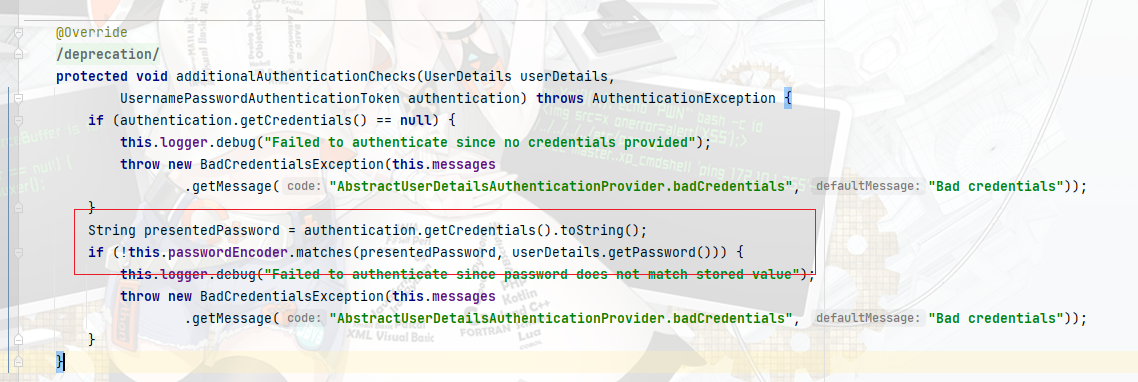
最后创建一个完整Authorization对象并返回给Granter,Granter处理后返回一个完整的OAuth2Authorization对象

3.然后回归到AbstractTokenGranter中,在前面的流程中我们已经拿到了完整的OAuth2Authorization对象,但是这个只是包含一个存储在上下文的方便OAuth使用的身份验证,但是之后返回需要的是令牌,需要令牌来认可操作的合法性,OAuth令牌即OAuthAccessToken DefaultOAuth2AccessToken为其默认实现
public class DefaultOAuth2AccessToken implements Serializable, OAuth2AccessToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 914967629530462926L;
/*
* token 值
*/
private String value;
/*
* 过期时间
*/
private Date expiration;
/*
* token 类型
*/
private String tokenType = BEARER_TYPE.toLowerCase();
/*
* 刷新token实体
*/
private OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken;
/*
* scope权限
*/
private Set<String> scope;
/*
*自定义信息相关
*/
private Map<String, Object> additionalInformation = Collections.emptyMap();
}
再回归到tokenServices.createAccessToken()方法,前面了解到,tokenServices是自定义令牌的持久化策略刷新策略等方案类.而在OAuth默认的配置类中,tokenServices默认注入的是DefaultTokenServices,这个类实现了
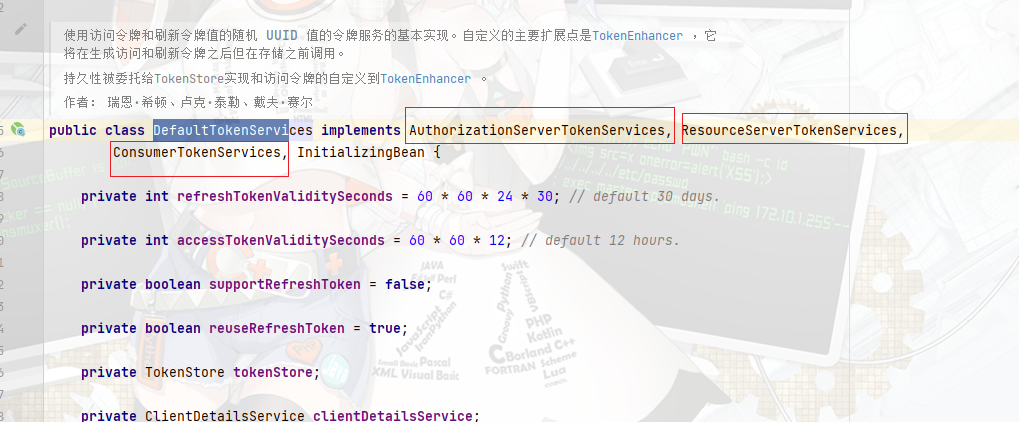
这三者接口的方法,这三个接口后续梳理,而createAccessToken()是AuthorizationServerTokenServices接口类的实现
梳理下来,创建令牌的流程如下
-
判断持久层是否存在令牌
-
如果存在且过期,那么就将过期的令牌删除掉
-
如果存在,但是没过期,那么就只需要更新下持久层的相关信息即可然后直接返回令牌,流程结束
-
-
根据逻辑组装令牌信息
-
存储到持久层并返回
//DefaultTokenServices
@Transactional
public OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
//从tokenStore查询是否已经存在OAuth2AccessToken
OAuth2AccessToken existingAccessToken = tokenStore.getAccessToken(authentication);
OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = null;
//如果不为空
if (existingAccessToken != null) {
//如果存在且过期了,那么就把store中存储的token相关信息都删除掉
if (existingAccessToken.isExpired()) {
if (existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken() != null) {
refreshToken = existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken();
// 这一步是官方为了保险起见,removeAccessToken会顺带删除......
tokenStore.removeRefreshToken(refreshToken);
}
tokenStore.removeAccessToken(existingAccessToken);
}
else {
//因为,没过期就更新下信息,再存储生成token信息
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(existingAccessToken, authentication);
return existingAccessToken;
}
}
/*
*如果不存在与过期访问令牌关联的现有刷新令牌,则仅创建新的刷新令牌。客户端可能持有现有的刷新令牌,因此我们在旧访问令牌过期的情况下重新使用它
*如果refreshToken为空,就创建refreshToken
*/
if (refreshToken == null) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
else if (refreshToken instanceof ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) {
ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken expiring = (ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) refreshToken;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > expiring.getExpiration().getTime()) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
}
// 创建访问令牌(还没存储到持久层中)
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = createAccessToken(authentication, refreshToken);
//保存相关信息(保存到持久层)
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(accessToken, authentication);
refreshToken = accessToken.getRefreshToken();
if (refreshToken != null) {
tokenStore.storeRefreshToken(refreshToken, authentication);
}
return accessToken;
}
到这里Spring Security OAuth 的认证流程也结束, 后续相关类的释义细节在认识模块中具体分析
三者之间的关系
至此,关于三者的介绍就都完成了,顺序读下来,一些概念其实已经跃然于屏幕上,OAuth2.0 是一个协议,Spring Security 是Spring实现的安全框架,Spring Security OAuth 是基于Spring Security 基础 和OAuth2.0协议标准的理论指导而综合设计而成.依赖于前两者的指导
比如,参数标准和流程是OAuth2.0的规则,Spring Security OAuth也按照标准实行了,Spring Security的认证基础是通过AuthorizationManager 寻找合适的Proivder来处理认证请求,并将从持久层得到的数据,封装成Authorization对象,而Spring Security OAuth 基于这一套逻辑完成了认证的基本流程得到Authorization对象,并封装成适合OAuth的OAuth2Authorization对象,并使用OAuth2Authorization对象创建生成OAuth2AccessToken令牌对象,持久化到持久层中
认识 Spring Security OAuth
目标
前面我们只是简单的认识了下流程,这节需要对类的定位有清楚的认知,才能去更好的实现下一步的改造OAuth的计划
认识
AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter
在Spring中 以Adapter结尾的统一都是适配器 ,基于设计模式,简单来说就是将两个不兼容的类整合在一起使用,两个类身份可以都属于框架源码,一个属于框架源码一个是自己编写的逻辑,也可以都是自己编写的逻辑,Adapter模式就是提供一个转化的作用
这里起配置集中认证服务器管理的作用,同时提供扩展的接口
AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter 提供了三个转换的接口,分别是
AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer用于配置安全设置相关,默认OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurationClientDetailsServiceConfigurer客户端定义类AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer配置授权服务器端点的属性和增强功能。
/**
* AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
public class AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter implements AuthorizationServerConfigurer {
/**
* 用于配置安全相关信息
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 配置clientDeails相关,提供来源支持
* 如内存 / JDBC 查询获得ClientDetails
*/
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 配置授权服务器端点的属性和增强功能,进行默认的初始化
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
}
}
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration
认证服务器配置类,初始化部分信息并注入部分配置
/**
* 设置关心的默认属性
*/
@Configuration
// 使用了EnableAuthorizationServer 才会使用,即只有在classpath存在该类才会启用
@ConditionalOnClass(EnableAuthorizationServer.class)
// 保证AuthorizationServerConfigurer及其实现只会被注入一次
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AuthorizationServerConfigurer.class)
//当AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration存在时,则实例化当前类 jwt
@ConditionalOnBean(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfiguration.class)
//注入AuthorizationServerProperties @ConfigurationProperties 注解的类 jwt
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AuthorizationServerProperties.class)
//注入AuthorizationServerTokenServicesConfiguration类
@Import(AuthorizationServerTokenServicesConfiguration.class)
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration
extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration.class);
private final BaseClientDetails details;
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private final TokenStore tokenStore;
private final AccessTokenConverter tokenConverter;
private final AuthorizationServerProperties properties;
public OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration(BaseClientDetails details,
AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration,
ObjectProvider<TokenStore> tokenStore,
ObjectProvider<AccessTokenConverter> tokenConverter,
AuthorizationServerProperties properties) throws Exception {
this.details = details;
this.authenticationManager = authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
this.tokenStore = tokenStore.getIfAvailable();
this.tokenConverter = tokenConverter.getIfAvailable();
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
// 默认从内存中拿取ClientDetail信息,并初始化其他信息
ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<InMemoryClientDetailsServiceBuilder>.ClientBuilder builder = clients
.inMemory().withClient(this.details.getClientId());
builder.secret(this.details.getClientSecret())
.resourceIds(this.details.getResourceIds().toArray(new String[0]))
.authorizedGrantTypes(
this.details.getAuthorizedGrantTypes().toArray(new String[0]))
.authorities(
AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(this.details.getAuthorities())
.toArray(new String[0]))
.scopes(this.details.getScope().toArray(new String[0]));
if (this.details.getAutoApproveScopes() != null) {
builder.autoApprove(
this.details.getAutoApproveScopes().toArray(new String[0]));
}
if (this.details.getAccessTokenValiditySeconds() != null) {
builder.accessTokenValiditySeconds(
this.details.getAccessTokenValiditySeconds());
}
if (this.details.getRefreshTokenValiditySeconds() != null) {
builder.refreshTokenValiditySeconds(
this.details.getRefreshTokenValiditySeconds());
}
if (this.details.getRegisteredRedirectUri() != null) {
builder.redirectUris(
this.details.getRegisteredRedirectUri().toArray(new String[0]));
}
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints)
throws Exception {
// 注入身份信息与令牌转换器配置
if (this.tokenConverter != null) {
endpoints.accessTokenConverter(this.tokenConverter);
}
// 注入令牌持久层策略
if (this.tokenStore != null) {
endpoints.tokenStore(this.tokenStore);
}
// 因为默认为密码模式,如果包含密码模式,就注入当前的authenticationManager
if (this.details.getAuthorizedGrantTypes().contains("password")) {
endpoints.authenticationManager(this.authenticationManager);
}
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security)
throws Exception {
//设置Encoder
security.passwordEncoder(NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
if (this.properties.getCheckTokenAccess() != null) {
security.checkTokenAccess(this.properties.getCheckTokenAccess());
}
//设置令牌端点是否开放 oauth/token ps: 默认无法访问denyAll()
if (this.properties.getTokenKeyAccess() != null) {
security.tokenKeyAccess(this.properties.getTokenKeyAccess());
}
//设置realm 默认无法访问denyAll()
if (this.properties.getRealm() != null) {
security.realm(this.properties.getRealm());
}
}
/**
* 设置默认的ClientDetails信息
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(BaseClientDetails.class)
protected static class BaseClientDetailsConfiguration {
private final OAuth2ClientProperties client;
protected BaseClientDetailsConfiguration(OAuth2ClientProperties client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "security.oauth2.client")
public BaseClientDetails oauth2ClientDetails() {
BaseClientDetails details = new BaseClientDetails();
if (this.client.getClientId() == null) {
this.client.setClientId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
details.setClientId(this.client.getClientId());
details.setClientSecret(this.client.getClientSecret());
details.setAuthorizedGrantTypes(Arrays.asList("authorization_code",
"password", "client_credentials", "implicit", "refresh_token"));
details.setAuthorities(
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_USER"));
details.setRegisteredRedirectUri(Collections.<String>emptySet());
return details;
}
}
ClientDetails
定义clientId所对应客户端实体属性
* Client details for OAuth 2
*
* @author Ryan Heaton
*/
public interface ClientDetails extends Serializable {
/**
* The client id.
*/
String getClientId();
/**
* 当前客户端具有的资源ID集合
*/
Set<String> getResourceIds();
/**
* 是否使用客户端密钥
*/
boolean isSecretRequired();
/**
* 客户端秘钥
*
* @return The client secret.
*/
String getClientSecret();
/**
* 是否使用scope字段
*/
boolean isScoped();
/**
* scope权限
*/
Set<String> getScope();
/**
* client能认证的列表
*/
Set<String> getAuthorizedGrantTypes();
/**
* 授权码模式跳转uri
*/
Set<String> getRegisteredRedirectUri();
/**
* 权限集合
*/
Collection<GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
/**
* 令牌有效时间
*
*/
Integer getAccessTokenValiditySeconds();
/**
* 刷新令牌有效时间
*/
Integer getRefreshTokenValiditySeconds();
/**
* 是否自动批准权限scope
*/
boolean isAutoApprove(String scope);
/**
* 附加描述信息,可自定义
*/
Map<String, Object> getAdditionalInformation();
}
ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer
ClientDetails类定义来源
/**
* @author Rob Winch
*
*/
public class ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer extends
SecurityConfigurerAdapter<ClientDetailsService, ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<?>> {
public ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer(ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<?> builder) {
setBuilder(builder);
}
public ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<?> withClientDetails(ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService) throws Exception {
setBuilder(getBuilder().clients(clientDetailsService));
return this.and();
}
public InMemoryClientDetailsServiceBuilder inMemory() throws Exception {
InMemoryClientDetailsServiceBuilder next = getBuilder().inMemory();
setBuilder(next);
return next;
}
public JdbcClientDetailsServiceBuilder jdbc(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
JdbcClientDetailsServiceBuilder next = getBuilder().jdbc().dataSource(dataSource);
setBuilder(next);
return next;
}
@Override
public void init(ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<?> builder) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceBuilder<?> builder) throws Exception {
}
}
AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer
提供安全的访问规则和相关信息配置注入,提供一个注入行为
/**
* 方法已删减
*/
public final class AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer extends
SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> {
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
private AccessDeniedHandler accessDeniedHandler = new OAuth2AccessDeniedHandler();
// 密码处理
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; // for client secrets
//realm
private String realm = "oauth2/client";
private boolean allowFormAuthenticationForClients = false;
//token链接/oauth/token 访问策略
private String tokenKeyAccess = "denyAll()";
//校验token链接/oauth//check_token 访问策略
private String checkTokenAccess = "denyAll()";
private boolean sslOnly = false;
/**
*TokenEndpoint 的自定义身份验证过滤器 默认在BasicAuthenticationFilter上游
*/
private List<Filter> tokenEndpointAuthenticationFilters = new ArrayList<Filter>();
}
AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer
授权服务器端点的属性和增强功能,提供一个注入行为
/**
*代码已简化, 对所列的属性进行注入,提供一个注入行为,后续讨论相关作用
*/
public final class AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer {
// 标准3TokenSerices之一
private AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices;
// 标准3TokenSerices之一
private ConsumerTokenServices consumerTokenServices;
// 授权码模式使用
private AuthorizationCodeServices authorizationCodeServices;
// 标准3TokenSerices之一
private ResourceServerTokenServices resourceTokenServices;
// 存储方案
private TokenStore tokenStore;
// token增强
private TokenEnhancer tokenEnhancer;
// OAuthToken转换器
private AccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter;
// 用于保存、检索和撤销用户批准的界面(每个客户端、每个范围)。
private ApprovalStore approvalStore;
// 绑定grant
private TokenGranter tokenGranter;
// OAuth2Request请求构建工厂
private OAuth2RequestFactory requestFactory;
// 验证请求scope是否合法
private OAuth2RequestValidator requestValidator;
// 授权码模式使用 客户端请求身份验证是否已被当前用户批准
private UserApprovalHandler userApprovalHandler;
// 认证管理器
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
// 客户端管理
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
private String prefix;
private Map<String, String> patternMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 允许认证端点请求的类型 POST GET 等等
private Set<HttpMethod> allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods = new HashSet<HttpMethod>();
// 框架端点的处理程序映射
private FrameworkEndpointHandlerMapping frameworkEndpointHandlerMapping;
// 是否禁用保存授权,会抛出异常
private boolean approvalStoreDisabled;
// 拦截器列表
private List<Object> interceptors = new ArrayList<Object>();
// token策略
private DefaultTokenServices defaultTokenServices;
// 获取用户信息
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private boolean tokenServicesOverride = false;
private boolean userDetailsServiceOverride = false;
private boolean reuseRefreshToken = true;
//响应重写翻译
private WebResponseExceptionTranslator<OAuth2Exception> exceptionTranslator;
//重定向解释器
private RedirectResolver redirectResolver;
}
以上是对认证服务器工作方式的解释,而WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter是对用户身份验证的安全方式解释,是对Spring Security的解释
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
一般用于配置资源权限管理, 最终会被AutowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents 初始化生成一个SecurityFilterChain拦截器类,作为过滤器处理请求进入spring后进行的认证操作.在认证服务器中做对于认证权限的管理
主要使用这三个方法
- configure(WebSecurity web): 一般配置全局安全性定制化/比如静态资源相关
- configure(HttpSecurity http): 在资源级访问配置权限的定制化
- configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth): 构建
AuthenticationManager相关属性
public abstract class WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter implements WebSecurityConfigurer<WebSecurity> {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class);
private ApplicationContext context;
private ContentNegotiationStrategy contentNegotiationStrategy = new HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy();
private ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor = new ObjectPostProcessor<Object>() {
@Override
public <T> T postProcess(T object) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ObjectPostProcessor.class.getName()
+ " is a required bean. Ensure you have used @EnableWebSecurity and @Configuration");
}
};
private AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration;
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder;
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder localConfigureAuthenticationBldr;
private boolean disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr;
private boolean authenticationManagerInitialized;
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver = new AuthenticationTrustResolverImpl();
private HttpSecurity http;
private boolean disableDefaults;
/**
* 构建AuthenticationManager相关属性
*/
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = true;
}
/**
* 一般配置全局安全性定制化/比如静态资源相关
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 在资源级访问配置权限的定制化
*/
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated());
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
}
/*
* 事件推送
*/
private AuthenticationEventPublisher getAuthenticationEventPublisher() {
if (this.context.getBeanNamesForType(AuthenticationEventPublisher.class).length > 0) {
return this.context.getBean(AuthenticationEventPublisher.class);
}
return this.objectPostProcessor.postProcess(new DefaultAuthenticationEventPublisher());
}
/**
* 创建公用的类
*/
private Map<Class<?>, Object> createSharedObjects() {
Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects = new HashMap<>();
sharedObjects.putAll(this.localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.getSharedObjects());
sharedObjects.put(UserDetailsService.class, userDetailsService());
sharedObjects.put(ApplicationContext.class, this.context);
sharedObjects.put(ContentNegotiationStrategy.class, this.contentNegotiationStrategy);
sharedObjects.put(AuthenticationTrustResolver.class, this.trustResolver);
return sharedObjects;
}
}
可以说这两个适配器类是构建认证服务器的核心
ResourceServerConfigurer
OAuth2资源身份验证与各种安全过滤器配置,与WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter作用相似
public class ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter implements ResourceServerConfigurer {
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
OAuth2Authentication
同Security中Authentication作用,但是OAuth2Authentication含有Authentication属性
OAuth2AccessToken
定义令牌的接口,默认实现为DefaultOAuth2AccessToken
OAuth2Request
代表OAuth2Request请求,存储授权或者令牌的请求信息,当为客户端时Authorization信息为空
AuthorizationRequest
在授权端点使用,代表OAuth2客户端的授权请求
AuthenticationEntryPoint
实现类用户请求处理中,在返回前,对异常做处理
* Token
实现AbstractAuthenticationToken 代表某一类授权类型处理的Token
* AuthenticationProvider
接口类,子类负责对各自对应的授权类型做处理支持,被AuthenticationManager所管理调用
* TokenGranter
接口类,令牌授予者,定义令牌的处理逻辑,将Provider生成的Authentication对象转为OAuth上下文使用
* UserDetailsService
接口类,实现子类用于提供UserDetails对象,作为认证成功与否的依据
TokenService
接口类,子类定义令牌发放的处理及操作
TokenEnhancer
接口类,负责对令牌的增强处理
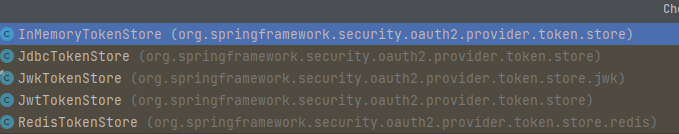
* TokenStore
接口类,根据系统定义确认如何持久化令牌,默认支持 内存/数据库/JWT/Redis
实现与改造 Spring Security OAuth
目标
这节的目的首先是对OAuth的基本功能作以实现,理解实现才能去确认如何改造



评论区